Central Africa
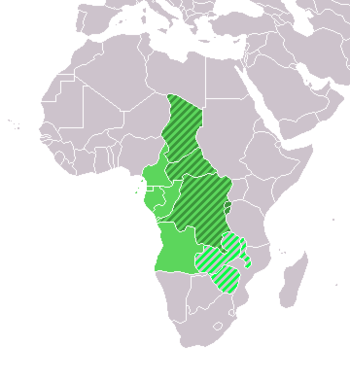
Central Africa is a core region of the African continent which includes Burundi, the Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Rwanda.
Middle Africa (as used by the United Nations when categorising geographic subregions) is an analogous term that includes Angola, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and São Tomé and Príncipe.[1] All of the states in the UN subregion of Middle Africa, plus those otherwise commonly reckoned in central Africa (11 states in total), comprise the Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS).[2]
The Central African Federation (1953–1963), also called the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, was made up of what are now the nations of Malawi, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Similarly, the Anglican Church of the Province of Central Africa covers dioceses in Botswana, Malawi, Zambia and Zimbabwe. These states are now typically regarded as parts of Southern Africa or Eastern Africa. [3]
See also
- British Central Africa Protectorate (1891–1907, now Malawi)
- French Equatorial Africa
- West Africa
- North Africa
- Southern Africa
- Subsaharan Africa
- History of a Central Africa
References
- ↑ "World Macro Regions and Components". United Nations. 2000. http://www.un.org/depts/dhl/maplib/worldregions.htm. Retrieved 2007-12-16.
- ↑ "Economic Community of Central African States". Africa-Union.org. 2007. http://www.africa-union.org/root/au/recs/eccas.htm. Retrieved 2007-12-16.
- ↑ "The Central African Federation". Encyclopedia Britannica. 2007. http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-43831/Southern-Africa. Retrieved 2007-12-16.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
External links
- Travel agency in Central Africa
- Africa Interactive Map from the United States Army Africa